Introduction
Welcome to the documents of TiKV Java Client. This document is oriented to:
-
Application developers who needs to integrate java client to their application code. There are documents about best practices, administrations, troubleshootings, and internals of TiKV Java Client for developers.
-
TiKV contributors who wish to contribute to TiKV Java Client, become a TiKV reviewer, committer, or maintainer. There are documents about setting up environment, submitting PR, triage issues, and manage releases in the community.
Wish you have a good journey in developing application or contributing to the TiKV Java Client.
Production Readiness
In general, the latest release of TiKV Java Client is ready for production use. But it is not battle-tested as full featured client for TiKV in all use cases. This page will give you more details.
RawKV
All RawKV APIs are covered by CI.
At this time, RawKV has been used in the production environment of some commercial customers in latency sensitive systems. But they only use part of the RawKV APIs (mainly including raw_put, raw_get, raw_compare_and_swap, and raw_batch_put).
TxnKV
All TxnKV APIs are covered by CI.
In addition, TxnKV has been used in the TiSpark and TiBigData project to integrate data from TiDB to Big Data ecosystem. TiSpark and TiBigData are used in the production system of some commercial customers and internet companies.
Similar to RawKV, only part of APIs are used in this scenario (mainly including prewrite/commit and coprocessor). And this use case doesn't care about latency but throughput and reliability.
TiDB Cloud
Directly using TiKV is not possible on TiDB Cloud due to the fact that client has to access the whole cluster, which has security issues. And TiKV managed service is not coming soon as it's not contained in roadmap yet.
Start With Examples
This section contains examples to demonstrate basic usages of the java client.
Quick Start
The package is hosted on maven central repository. To build from source, refer to the Contribution Guide.
Create a maven project
First download maven and follow the installation instructoins. Then mvn command should be available in the $PATH.
create a maven project by following command:
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.example -DartifactId=java-client-example -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DinteractiveMode=false
cd java-client-example
Add dependency
Add maven dependency to pom.xml.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.tikv</groupId>
<artifactId>tikv-client-java</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.32</version>
</dependency>
Now pom.xml should look like this:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>java-project</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>java-project</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.tikv</groupId>
<artifactId>tikv-client-java</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.32</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Writing code
To interact with TiKV, we should first create a TiConfiguration with PD address, create a TiSession using TiSession.create, and then create a client.
For example, if we want to put a World in Hello key in RawKV, write the following code in src/main/java/com/example/App.java.
import org.tikv.common.TiConfiguration;
import org.tikv.common.TiSession;
import org.tikv.raw.RawKVClient;
import org.tikv.shade.com.google.protobuf.ByteString;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String pdAddr = "127.0.0.1:2379";
// You MUST create a raw configuration if you are using RawKVClient.
TiConfiguration conf = TiConfiguration.createRawDefault(pdAddr);
try (TiSession session = TiSession.create(conf)) {
try (RawKVClient client = session.createRawClient()) {
client.put(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("Hello"), ByteString.copyFromUtf8("World"));
ByteString value = client.get(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("Hello"));
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
}
More examples for RawKV and TxnKV are in following chapters.
Running program
Run following command:
mvn assembly:assembly -DdescriptorId=jar-with-dependencies
java -cp target/java-client-example-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar com.example.App
RawKV
Below is the basic usages of RawKV. See API document to see a full list of methods available.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.tikv.common.TiConfiguration;
import org.tikv.common.TiSession;
import org.tikv.kvproto.Kvrpcpb;
import org.tikv.raw.RawKVClient;
import org.tikv.shade.com.google.protobuf.ByteString;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// You MUST create a raw configuration if you are using RawKVClient.
TiConfiguration conf = TiConfiguration.createRawDefault("127.0.0.1:2379");
TiSession session = TiSession.create(conf);
RawKVClient client = session.createRawClient();
// put
client.put(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k1"), ByteString.copyFromUtf8("Hello"));
client.put(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k2"), ByteString.copyFromUtf8(","));
client.put(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k3"), ByteString.copyFromUtf8("World"));
client.put(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k4"), ByteString.copyFromUtf8("!"));
client.put(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k5"), ByteString.copyFromUtf8("Raw KV"));
// get
Optional<ByteString> result = client.get(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k1"));
System.out.println(result.get().toStringUtf8());
// batch get
List<Kvrpcpb.KvPair> list = client.batchGet(new ArrayList<ByteString>() {{
add(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k1"));
add(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k3"));
}});
System.out.println(list);
// scan
list = client.scan(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k1"), ByteString.copyFromUtf8("k6"), 10);
System.out.println(list);
// close
client.close();
session.close();
}
}
API V2
With TiKV version >= 6.1.0, we release a new feature called "TiKV API V2" which provides a new raw key-value storage format allowing the coexistence of RawKV and TxnKV. Please refer to v6.10 release notes for detail.
To enable the API V2 mode, users need to specify the API version of the client.
// import ...
import org.tikv.common.TiConfiguration.ApiVersion;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TiConfiguration conf = TiConfiguration.createRawDefault("127.0.0.1:2379");
conf.setApiVersion(ApiVersion.V2);
try(TiSession session = TiSession.create(conf)) {
try(RawKVClient client = session.createRawClient()) {
// The client will read and write date in the format of API V2, which is
// transparent to the users.
client.put(ByteString.copyFromUtf8("hello"), ByteString.copyFromUtf8("world"));
// other client operations.
}
}
}
}
Compatibility
The V2 Client should not access the cluster other than V2, this requires users to enable the API V2 for the cluster:
[storage]
# The V2 cluster must enable ttl for RawKV explicitly
enable-ttl = true
api-version = 2
If V2 client accesses a V1 cluster or V1 cluster accesses a V2 cluster, the requests will be denied by the cluster. You can check the compatibility via the following matrix.
| V1 Server | V1TTL Server | V2 Server | |
|---|---|---|---|
| V1 RawClient | Raw | Raw | Error |
| V1 RawClient with TTL | Error | Raw | Error |
| V1 TxnClient | Txn | Error | Error |
| V1 TiDB | TiDB Data | Error | TiDB Data |
| V2 RawClient | Error | Error | Raw |
| V2 TxnClient | Error | Error | Txn |
TxnKV
Below is the basic usages of TxnKV.
Data should be written into TxnKV using TwoPhaseCommitter, and be read using org.tikv.txn.KVClient.
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.tikv.common.BytePairWrapper;
import org.tikv.common.ByteWrapper;
import org.tikv.common.TiConfiguration;
import org.tikv.common.TiSession;
import org.tikv.common.util.BackOffer;
import org.tikv.common.util.ConcreteBackOffer;
import org.tikv.kvproto.Kvrpcpb.KvPair;
import org.tikv.shade.com.google.protobuf.ByteString;
import org.tikv.txn.KVClient;
import org.tikv.txn.TwoPhaseCommitter;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TiConfiguration conf = TiConfiguration.createDefault("127.0.0.1:2379");
try (TiSession session = TiSession.create(conf)) {
// two-phrase write
long startTS = session.getTimestamp().getVersion();
try (TwoPhaseCommitter twoPhaseCommitter = new TwoPhaseCommitter(session, startTS)) {
BackOffer backOffer = ConcreteBackOffer.newCustomBackOff(1000);
byte[] primaryKey = "key1".getBytes("UTF-8");
byte[] key2 = "key2".getBytes("UTF-8");
// first phrase: prewrite
twoPhaseCommitter.prewritePrimaryKey(backOffer, primaryKey, "val1".getBytes("UTF-8"));
List<BytePairWrapper> pairs = Arrays
.asList(new BytePairWrapper(key2, "val2".getBytes("UTF-8")));
twoPhaseCommitter.prewriteSecondaryKeys(primaryKey, pairs.iterator(), 1000);
// second phrase: commit
long commitTS = session.getTimestamp().getVersion();
twoPhaseCommitter.commitPrimaryKey(backOffer, primaryKey, commitTS);
List<ByteWrapper> keys = Arrays.asList(new ByteWrapper(key2));
twoPhaseCommitter.commitSecondaryKeys(keys.iterator(), commitTS, 1000);
}
try (KVClient kvClient = session.createKVClient()) {
long version = session.getTimestamp().getVersion();
ByteString key1 = ByteString.copyFromUtf8("key1");
ByteString key2 = ByteString.copyFromUtf8("key2");
// get value of a single key
ByteString val = kvClient.get(key1, version);
System.out.println(val);
// get value of multiple keys
BackOffer backOffer = ConcreteBackOffer.newCustomBackOff(1000);
List<KvPair> kvPairs = kvClient.batchGet(backOffer, Arrays.asList(key1, key2), version);
System.out.println(kvPairs);
// get value of a range of keys
kvPairs = kvClient.scan(key1, ByteString.copyFromUtf8("key3"), version);
System.out.println(kvPairs);
}
}
}
}
Administration
Java Client Configuration Parameter
JVM Parameter
The following includes JVM related parameters.
tikv.pd.addresses
- pd addresses, separated by comma
- default: 127.0.0.1:2379
tikv.grpc.timeout_in_ms
- timeout of grpc request
- default: 600ms
tikv.grpc.scan_timeout_in_ms
- timeout of scan/delete range grpc request
- default: 20s
tikv.importer.max_kv_batch_bytes
- Maximal package size transporting from clients to TiKV Server (ingest API)
- default: 1048576 (1M)
tikv.importer.max_kv_batch_size
- Maximal batch size transporting from clients to TiKV Server (ingest API)
- default: 32768 (32K)
tikv.scatter_wait_seconds
- time to wait for scattering regions
- default: 300 (5min)
tikv.rawkv.default_backoff_in_ms
- RawKV default backoff in milliseconds
- default: 20000 (20 seconds)
Metrics Parameter
tikv.metrics.enable
- whether to enable metrics exporting
- default: false
tikv.metrics.port
- the metrics exporting http port
- default: 3140
ThreadPool Parameter
The following includes ThreadPool related parameters, which can be passed in through JVM parameters.
tikv.batch_get_concurrency
- the thread pool size of batchGet on client side
- default: 20
tikv.batch_put_concurrency
- the thread pool size of batchPut on client side
- default: 20
tikv.batch_delete_concurrency
- the thread pool size of batchDelete on client side
- default: 20
tikv.batch_scan_concurrency
- the thread pool size of batchScan on client side
- default: 5
tikv.delete_range_concurrency
- the thread pool size of deleteRange on client side
- default: 20
tikv.enable_atomic_for_cas
- whether to enable
Compare And Set, set true if usingRawKVClient.compareAndSetorRawKVClient.putIfAbsent - default: false
TLS
tikv.tls_enable
- whether to enable TLS
- default: false
tikv.trust_cert_collection
- Trusted certificates for verifying the remote endpoint's certificate, e.g. /home/tidb/ca.pem. The file should contain an X.509 certificate collection in PEM format.
- default: null
tikv.key_cert_chain
- an X.509 certificate chain file in PEM format, e.g. /home/tidb/client.pem.
- default: null
tikv.key_file
- a PKCS#8 private key file in PEM format. e.g. /home/tidb/client-key.pem.
- default: null
tikv.tls.reload_interval
- The interval in seconds to poll the change of TLS context, if a change is detected, the TLS context will be rebuilded.
- default:
"10s","0s"means disable TLS context reload.
tikv.conn.recycle_time
- After a TLS context reloading, the old connections will be forced to shutdown after
tikv.conn.recycle_timeto prevent channel leak. - default:
"60s".
tikv.rawkv.read_timeout_in_ms
- RawKV read timeout in milliseconds. This parameter controls the timeout of
getgetKeyTTL. - default: 2000 (2 seconds)
tikv.rawkv.write_timeout_in_ms
- RawKV write timeout in milliseconds. This parameter controls the timeout of
putputAtomicputIfAbsentdeletedeleteAtomic. - default: 2000 (2 seconds)
tikv.rawkv.batch_read_timeout_in_ms
- RawKV batch read timeout in milliseconds. This parameter controls the timeout of
batchGet. - default: 2000 (2 seconds)
tikv.rawkv.batch_write_timeout_in_ms
- RawKV batch write timeout in milliseconds. This parameter controls the timeout of
batchPutbatchDeletebatchDeleteAtomic. - default: 2000 (2 seconds)
tikv.rawkv.scan_timeout_in_ms
- RawKV scan timeout in milliseconds. This parameter controls the timeout of
batchScanscanscanPrefix. - default: 10000 (10 seconds)
tikv.rawkv.clean_timeout_in_ms
- RawKV clean timeout in milliseconds. This parameter controls the timeout of
deleteRangedeletePrefix. - default: 600000 (10 minutes)
Java Client Metrics
Client Java supports exporting metrics to Prometheus using poll mode and viewing on Grafana. The following steps shows how to enable this function.
Step 1: Enable metrics exporting
- set the config
tikv.metrics.enabletotrue - call TiConfiguration.setMetricsEnable(true)
Step 2: Set the metrics port
- set the config
tikv.metrics.port - call TiConfiguration.setMetricsPort
Default port is 3140.
Step 3: Config Prometheus
Add the following config to conf/prometheus.yml and restart Prometheus.
- job_name: "tikv-client"
honor_labels: true
static_configs:
- targets:
- '127.0.0.1:3140'
- '127.0.0.2:3140'
- '127.0.0.3:3140'
Step 4: Config Grafana
Import the Client-Java-Summary dashboard config to Grafana.
Troubleshooting
Slow Request Diagnosis
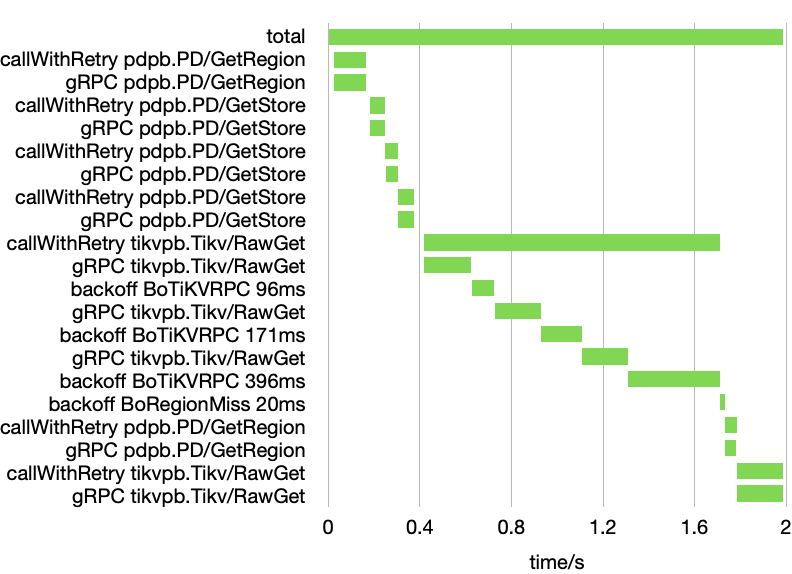
If a request take too much time, we can collect the detailed time spend in each component in a “slow log”.
2022-02-11 11:07:56 WARN SlowLogImpl:88 - A request spent 55 ms. start=11:07:56.938, end=11:07:56.993, SlowLog:{"trace_id":4361090673996453790,"spans":[{"event":"put","begin":"11:07:56.938","duration_ms":55,"properties":{"region":"{Region[2] ConfVer[5] Version[60] Store[1] KeyRange[]:[]}","key":"Hello"}},{"event":"getRegionByKey","begin":"11:07:56.938","duration_ms":0},{"event":"callWithRetry","begin":"11:07:56.943","duration_ms":49,"properties":{"method":"tikvpb.Tikv/RawPut"}},{"event":"gRPC","begin":"11:07:56.943","duration_ms":49,"properties":{"method":"tikvpb.Tikv/RawPut"}}]}
Slow log configurations
| SlowLog settings | default value |
|---|---|
| tikv.rawkv.read_slowlog_in_ms | tikv.grpc.timeout_in_ms * 2 |
| tikv.rawkv.write_slowlog_in_ms | tikv.grpc.timeout_in_ms * 2 |
| tikv.rawkv.batch_read_slowlog_in_ms | tikv.grpc.timeout_in_ms * 2 |
| tikv.rawkv.batch_write_slowlog_in_ms | tikv.grpc.timeout_in_ms * 2 |
| tikv.rawkv.scan_slowlog_in_ms | 5s |
Each settings can be set by system properties, configuration files or set... method of TiConfiguration.
System properties can be set by -D parameter of java command.
java -cp target/java-client-example-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar -Dtikv.rawkv.read_slowlog_in_ms=100 com.example.App
Configuration file is src/main/resources/tikv.properties in maven projects.
Visualize slow log
TBD
Architecture
This section includes in-depthA description of the client architecture.
The Lifecycle of A Request
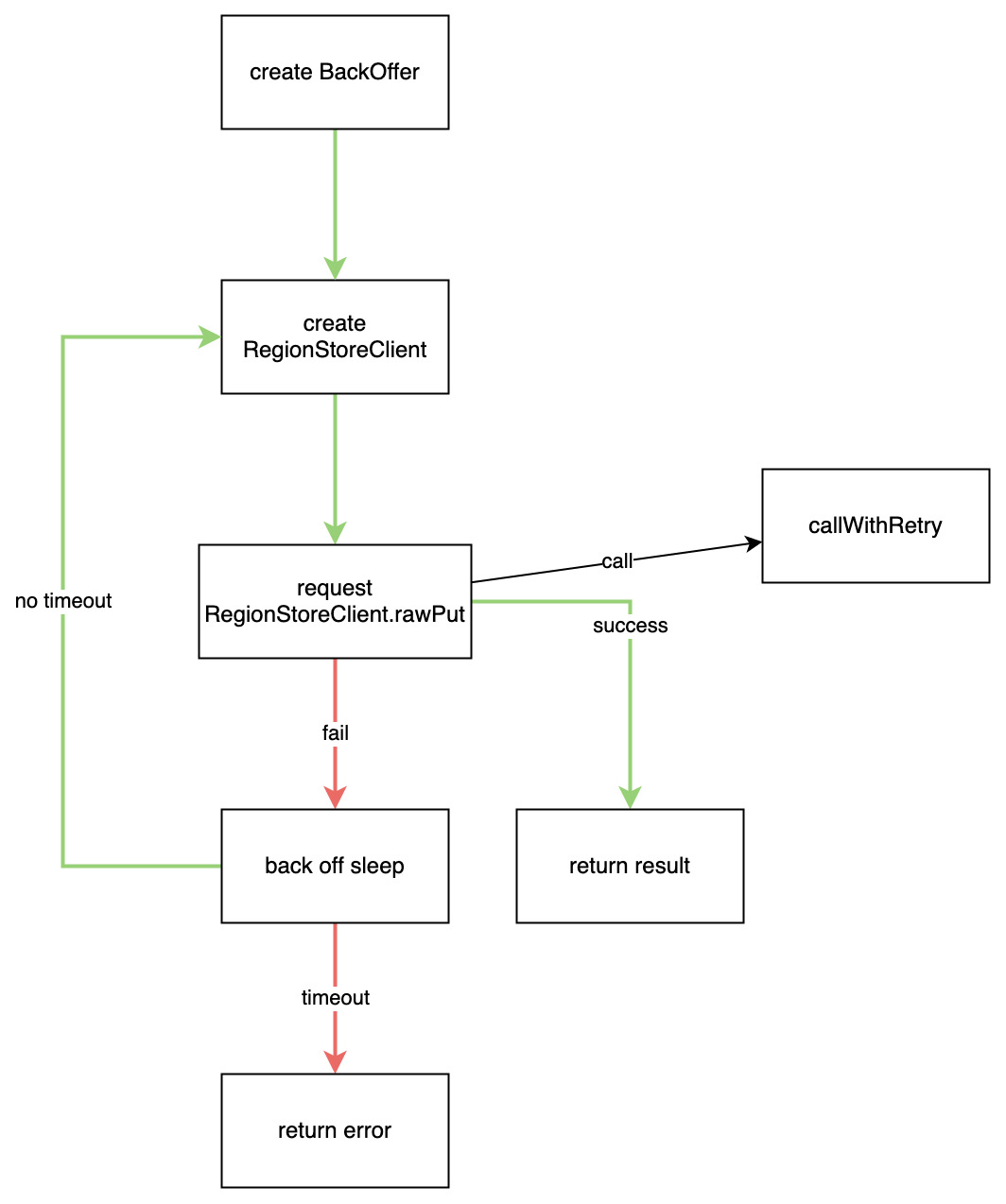
The client talks to TiKV store directly using gRPC requests, which are created in RegionStoreClient. If a request failed, the client could retry after a back off sleep. The retry logic is delegated to AbstractGRPCClient::callWithRetry method. callWithRetry may decide to retry request within the function, or, if the RegionStoreClient must be recreated (due to, for example, region split), return a failure and let outermost RawKVClient to do the retry.
Availability: Backoff and Retry Policy
BackOffer
The retry and timeout mechanism for a request is controlled by a BackOffer object, which is created one per RawKVClient method. The BackOffer will decide how much time the next sleep and retry should spend, and whether to timeout the request if not enough time is left for retrying the request.
If we need a back off sleep, we call backOffer.doBackOff(funcType, exception), and the current thread will sleep for a decided time. If the current operation will timeout after sleep, the doBackOff simply throw an exception to abort the operation.
callWithRetry
RegionStoreClient.callWithRetry inherits from AbstractGRPCClient.callWithRetry. The concrete logic is in RetryPolicy.callWithRetry, which implements a retry mechanism, but the specific retry strategy is determined by the ErrorHandler. ErrorHandler’s handler{Request, Response}Error function returns a boolean value indicating whether to retry inside callWithRetry. The control flow for callWithRetry is as follows:
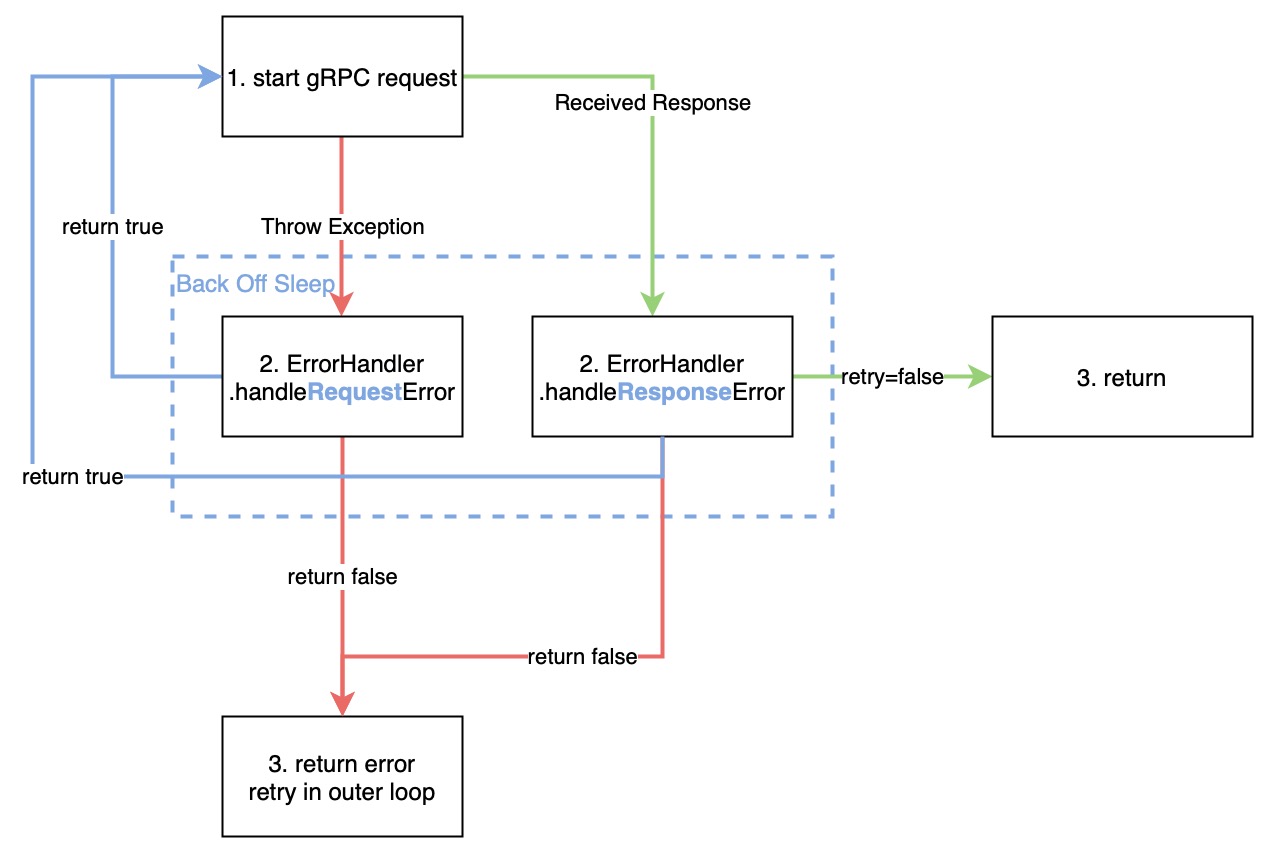
The error handler is chosen obeying the following table:
| gPRC request | the result | handler |
|---|---|---|
| throws exception | - | handleRequestError |
| no exception | is null | handleRequestError |
| no exception | is error | handleResponseError |
| no exception | normal | normal return |
The handleRequestError function copes with the following situations:
| situation | retry within callWithRetry | note |
|---|---|---|
| invalid store in region manager | true | refresh ClientStub |
| region has not got multiple copies | false | |
| successfully switched to new leader | true | |
| seekProxyStore | true if success | only when tikv.enable_grpc_forward is set |
| other | false |
The handleResponseError function copes with the following gRPC errors:
| error | retry within callWithRetry |
|---|---|
| NotLeader | true if leader unchanged |
| StoreNotMatch | false |
| EphochNotMatch | true if region epoch in ctx is ahead of TiKV's |
| ServerIsBusy | true |
| StaleCommand | true |
| RaftEntryTooLarge | throw |
| KeyNotInRegion | throw |
| Raft ProposalDropped | true |
| other | false |
Contribution Guide
Build the package
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true
Install the package to local maven repository
mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true
Run tests
export RAWKV_PD_ADDRESSES=127.0.0.1:2379
export TXNKV_PD_ADDRESSES=127.0.0.1:2379
mvn clean test
Bug Severity Guidelines
This is a working-in-progress guide about determining defects severity on TiKV Java Client according to the impact on the online service. The higher effect the defect has on the overall functionality or performance, the higher the severity is. There are 4 severity levels:
- Critical
- Major
- Moderate
- Minor
Each severity is described with examples in the remaining contents.
Critical Defects
A defect that affects critical data or functionality and leaves users
with no workaround is classified as a critical defect. These defects are
labeled with type/bug and severity/critical, can be found
here
Guideline 1. A defect that breaks the API definition is regarded as critical. For example:
- client-java/issues/412 in this defect, gRPC timeout is not set for certain requests, which causes the requests can not be terminated as expected when the processing time is too long.
Major Defects
A defect that affects critical data or functionality and forces users to employ
a workaround is classified as a major defect. These defects are labeled with
type/bug and severity/major, can be found
here
Moderate Defects
A defect that affects non-critical data or functionality and forces users to
employ a workaround is classified as moderate defect. These defects are labeled
with type/bug and severity/moderate, can be found
here
Minor Defects
A defect that does not affect data or functionality. It does not even need a
workaround. It does not impact productivity or efficiency. It is merely an
inconvenience. These defects are labeled with type/bug and severity/minor,
can be found
here